ERP Implementation: Key Phases You’d Want to Consider
ERP Implementation: Key Phases You’d Want to Consider

Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems have become essential tools for organizations seeking to optimize their business processes, improve productivity, and gain a competitive edge. Companies such as Nestlé, Siemens, and BMW are successful cases of ERP implementation.
Implementing an ERP system is a complex undertaking that requires careful planning, coordination, and expertise. In this article, we will explore the key aspects of ERP implementation, its main stages, and the relevance of finding the right partner.
What is an ERP implementation?
ERP implementation refers to the process of introducing and integrating an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system into an organization’s operations. The whole process normally takes a few months and it’s complex as it involves planning, customizing, configuring, testing, training, and deploying the ERP software to effectively manage and streamline business processes.
Focal points for an ERP implementation
To ensure successful deployment and maximize the benefits of an ERP system, it is crucial to prioritize key focal points during implementation. By directing your attention to these areas, you can significantly increase the likelihood of a favorable outcome. It is important to tailor the implementation approach to suit your organization’s unique requirements and attributes for optimal results. Presented below is a chart outlining the three primary focal points that should be taken into consideration:
| Change Management | Employees must be trained on how to use the new system, and managers must be equipped to support them through the transition. Provide hands-on training sessions, user documentation, and ongoing support to facilitate smooth user adoption. |
| Data Preparation and Migration | Ensure that your data is properly prepared and cleansed before migration to the new ERP system. Develop a data migration plan, including mapping data from existing systems to the new system. *Note: Test the process to validate data accuracy and integrity. |
| Project Management | Develop a detailed implementation plan, including timelines, milestones, and resource allocation. Assign a dedicated project manager to oversee the implementation and ensure coordination among all stakeholders involved. Regularly monitor and evaluate the project’s progress to stay on track. |
Stages of an ERP Implementation
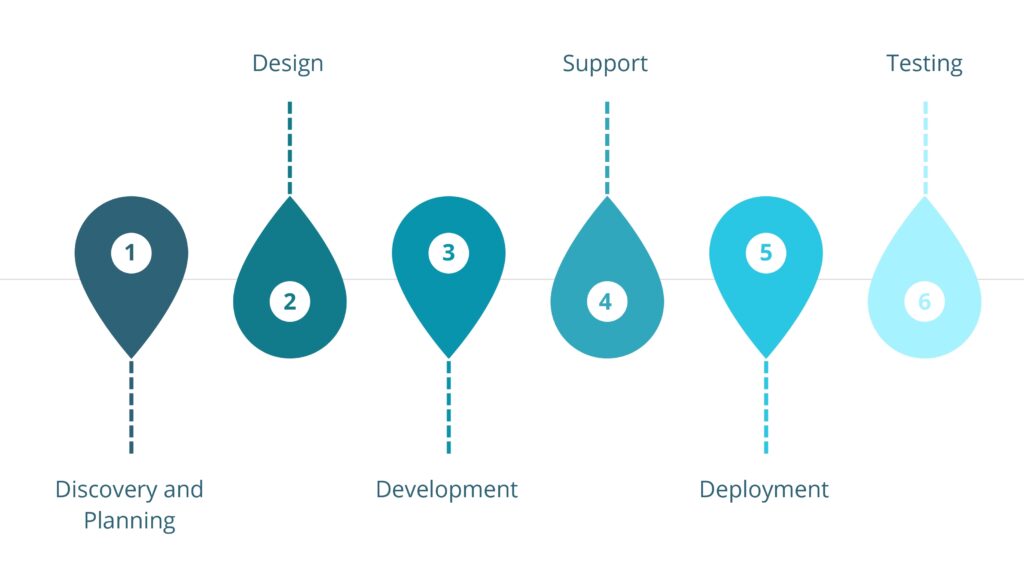
Implementing an ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) system typically involves several key stages. Here’s the journey of an ERP implementation:
1. Planning and Preparation:
- Define and identify the project’s scope, objectives, desired outcomes, and stakeholders.
- Conduct a comprehensive analysis of the organization’s current processes, systems, and data.
- Research and evaluate ERP vendors to choose the most suitable solution for the organization’s requirements.
- Develop a detailed project plan, including timelines, milestones, resource allocation, and budget. Define the implementation strategy and establish clear roles and responsibilities within the project team.
2. System Configuration and Customization: Once the planning and preparation stage is complete, the focus shifts to configuring and customizing the ERP system to align with the organization’s specific requirements. This stage involves:
- Set up the ERP system by configuring modules, defining workflows, and establishing user access controls.
- Transfer data from legacy systems to the new ERP system. This includes data cleansing, mapping, and validation to ensure the accuracy and integrity of the data.
- Adapt the ERP system to meet unique business needs. This may involve developing custom reports, integrating third-party applications, or modifying certain functionalities within the system.
- Conduct thorough testing to verify that the ERP system functions as expected.
3. Training, Go-Live, and Post-Implementation: The final stage involves preparing the organization for the system’s go-live and providing ongoing support.
- Provide comprehensive training programs for employees to understand and effectively use the ERP system.
- Implement the ERP system in the live production environment. This involves transitioning from the legacy systems to the new ERP system and ensuring a smooth transfer of operations.
- Adopt ongoing support and maintenance after the go-live phase. This includes addressing user inquiries, resolving issues or bugs, providing system updates, and continuously monitoring system performance.
What is SAP and what does it stand for?
SAP stands for Systems, Applications, and Products in Data Processing. SAP’s software solutions cover various domains, including ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning), CRM (Customer Relationship Management), SCM (Supply Chain Management), HR (Human Resources), and more. SAP’s flagship ERP product, SAP ERP, is widely used by large enterprises worldwide to integrate and automate their business processes.
SAP Business One
SAP Business One is an ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) solution specifically designed for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). It provides comprehensive functionalities to manage various aspects of business operations, including finance, sales, inventory, purchasing, customer relationship management (CRM), and reporting. SAP Business One offers scalability, flexibility, and integration capabilities, enabling SMEs to streamline processes, improve efficiency, and make data-driven decisions to drive growth and profitability.
Why is it essential to have the right partner?
Selecting the right ERP implementation partner is vital to ensure a successful ERP implementation. They provide expertise, guidance, customization, training, ongoing support, and risk mitigation, resulting in a well-executed implementation that maximizes the benefits of the ERP system and sets the organization on a path to success.

